Hey everyone 👋 — I’m Avirath. I learn a lot from reading S1 teardowns, company analysis reviews, IPO previews. I wanted to share this knowledge with my readers - that’s the motive behind this newsletter.
This article breaks down Epic and its bull and bear cases inspired by Erik Torenberg and Avidan Rudansky
If you are interested in receiving future content from me directly in your inbox, consider subscribing 👇.
Join the fun on Twitter.
It was the peak of a sultry lockdown afternoon as I lazily slumbered on my bed. I was only going to sleep when I hear my 10 year old brother yell “Jump”, “Shoot”, “Shoot again”. Accompanying his screams were alien like gun noises. The commotion piqued my interest and I go to the living room to see what the ruckus was about. My brother is shooting away in a vivid, eye-catching and first player world. The vast expanse of the map, the detail to in-game architecture and the complex yet smooth physics of the game meant just one thing - twenty five minutes of adrenaline frenzy battle royal style. However, I didn’t pay too much attention thinking it was one of those fads that’d die over.
I was wrong. Three years later, the game has amassed about 400M users and generates about 5.4 billion dollars of revenue for its parent company. That game is Fortnite and its parent company is Epic Games.
Epic Games is one of the most popular, powerful and technically advanced gaming platforms in the world with immense potential to grow in the coming digital future. Its greatest strength lies in the end-to-end vertically integrated system including the Unreal Engine, the Epic Games Store and Epic Online Services it provides for users to develop games, sell them and maintain them through their lifetime.
Products
Fortnite
Fortnite is rightly known as Epic’s flagship product as it boasts 400 million lifetime users and close to 80 million monthly active users(MAUs). What started off as a battle royal first player shooting frenzy now holds the key for Epic’s quest into the metaverse. It has three different player modes as such:
Battle Royal
Fortnite’s most loved game mode where players land on a remote island and use a combination of construction and shooting skills to be the last player standing.
Party Mode
Similar to Club Penguin, Fortnite’s Party Mode allows users to project themselves in a digital world using avatars and special clothing items where they can digitally “hang out” with players and attend music concerts such as the one Epic held with Travis Scott.
Creative Mode
Players can create worlds and other games using the underlying principles and assets of Fortnite like Roblox and Minecraft allow.
Fortnite’s 80 million MAUs is no mean feat. This would imply it has the third highest monthly active user base after Roblox and Minecraft that boast 220 million and 140 million number of monthly active users for a game that is 7 years younger. Where Fortnite completely dominates competitors is time spent on the platform where it has amassed an additional 1.2 billion hours compared to Roblox and Minecraft. For Epic’s ambition to lead the metaverse, it needs to become the digital social townplace which would mean users immerse themselves in the Fortnite metaverse experience and stay there for hours. This heuristic looks on the upside for Epic as analyst Matthew Ball writes that users spend 3x the time on Fortnite compared to other social apps like Snapchat or Instagram.
Unreal Engine
A game engine is a set of software frameworks primarily designed for development of video games and supporting libraries. In recent years, these robust frameworks have grown to become very useful in architecture, film development and interior designing. Unreal Engine, with around a 15% market share, is one of the most technically advanced and liked game engines in the world
In its 25 years history, Unreal has added features such as Metahuman Creator Tool(a tool to create high definition humanlike characters), the World Creator Tool(tool to create 3D immersive divisible worlds) and developed tools that can integrate several custom libraries to make game development personalized.
Epic Games Store
Gaming ecosystems on the phone and desktop developed in different ways. On the mobile, inbuilt app stores like the App Store on iOS and the Google Play Store on Android became the default stores to purchase games from. These stores charged a 30% commission on all revenue made by any game.
On the desktop, Windows supported devices were chosen to be the “go-to” standard for game development and play over Apple’s line of computers due to their distribution scale, backwards compatibility and the macOS having very different gaming development rules compared to Windows.
However, unlike other apps, games require a lot of other downloaded infrastructure including payment processors, image visualization libraries, external hard drives. Further, most PCs don’t have enough storage for multiple games. To solve this issue, Valve launched Steam in 2003. Steam is a digital distribution platform for video games and also provides features such as social networking, in-game voice and chat functionality, cloud saving, and automatic updates for games. All of these features were provided to users and publishers for free but in the process, Steam developed a wide array of network effects. Like most distribution platforms, Steam took a 30% transaction fee.
After the success of Fortnite, Epic entered the gaming distribution market by undercutting Steam’s 30% revenue cut to just 12%. Epic also employed the tactic of using time exclusivity agreements where games would only be available on the Epic Games Store while Epic provided these game publishers minimum revenue agreements. EGS recorded 31.3 million daily active users(DAUs) in 2020.
Market Model
Epic's business model is built around a multi-faceted approach that includes game development, digital distribution, and game engine technology. Epic Games is best known for its flagship game, Fortnite, which has become a cultural phenomenon and a significant revenue generator for the company. Recently, it’s been using the hefty revenues generated in Fortnite to create several revenue opportunities through the means of a Games Store and Online Services platform along with its original game engine, Unreal.
Fortnite
Fortnite is a free to play game model. Fortnite generates most of its income from the sale of virtual items that do not impact gameplay, such as costumes and avatars, as well as Battle Passes that offer rewards and new accessories every season. To make in-app purchases, players must use Fortnite's own currency, called "V-bucks." The "free-to-play" approach of Fortnite differs significantly from the traditional model of free games. This is because Fortnite's virtual items do not provide any advantage within the game, which makes the system feel fair and equitable.
Unreal Engine
Royalties and licensing are the two ways that Unreal Engine makes money. Despite the fact that UE's source code is publicly accessible on GitHub, if a developer makes more than $1 million in gross revenue, UE's owner, Epic Games, will take a 5% royalty on any product that uses UE code. However, Epic Games will forego the royalty payment and take home a larger payment if the game is sold on the Epic Games Store. UE offers Standard, Enterprise, and Custom license types. Standard licenses are free, but a 5% royalty is expected. Enterprise licenses cost $1,500 per seat per year and provide more specialized training and support. Custom licenses are created to meet the unique requirements of a business.
Epic Games Store
The Epic Games Store levies a 12% commission on game sales, but due to the expenses associated with their "minimum guarantee" program and the weekly free games they provide, the company is operating at a loss. Even though it means losing money, Epic pays for timed exclusivity contracts to entice developers and publishers. Additionally, they fully subsidize the free games they provide, which according to some estimations totaled around 765 million and were worth roughly $18 billion in 2021. Epic Games Store consequently reported losses of $139 million in 2021 and $273 million in 2020.
Opportunities/The Bull Case
Technological Superiority
In the early years of gaming, most games were designed and developed specifically for one particular platform, such as a Super Nintendo console, or PlayStation gaming system. Today, most games aspire to be on as many platforms as possible. Each platform has its own compatibility rules which can make it hard to develop multi-platform games but Unreal Engine eliminates this worry.
In addition to this, Unreal benefits from its wide array of features and network effects. It offers solutions for almost all major tasks you may encounter in game development, such as designing scenes with landscapes and foliage, creating cinematic sequences, using visual scripting, implementing particle effects, creating animations, managing assets, generating lightmaps, controlling level of detail, implementing physics, building AI, and tracking performance and memory usage. The sheer number of features has helped Epic not only host big game titles such as Valorant and the Batman series but also expand into content creation, education and modern architecture.
This was evidenced by the large role Unreal played in virtual set generation for the 2019 popular release - the Mandalorian. With Unreal Engine and dedicated operators on the backend, director Jon Favreau and technical staff working on the Mandalorian could change the visual backdrop of the virtual screen against which the show was shot to the nearest pixel. It was critical to the show’s ability to offer film-grade visuals at half a film budget and more than twice the running time. However, it also offered unique cinemagraphic flexibility since changing the scenes behind just meant shifting between screens/backdrops on Unreal. It’s true that Unity supports more mobile game apps than Unreal does and they both differ in their pricing models where Unity charges developers a subscription fee and Unreal takes a 5% revenue cut for anything developed on Unreal. The global animation market size is expected to hit around US$ 642.5 bn by 2030, growing at a CAGR of 5.2% from 2021 to 2030. If Unreal became as essential as it is to hi-fi games to video content creation, that would mean a lot of top-line growth.
Over the years, a lot of architecture firms and automotive firms have begun to work with Unreal on prototyping, iteration and modeling as well.
Metaverse
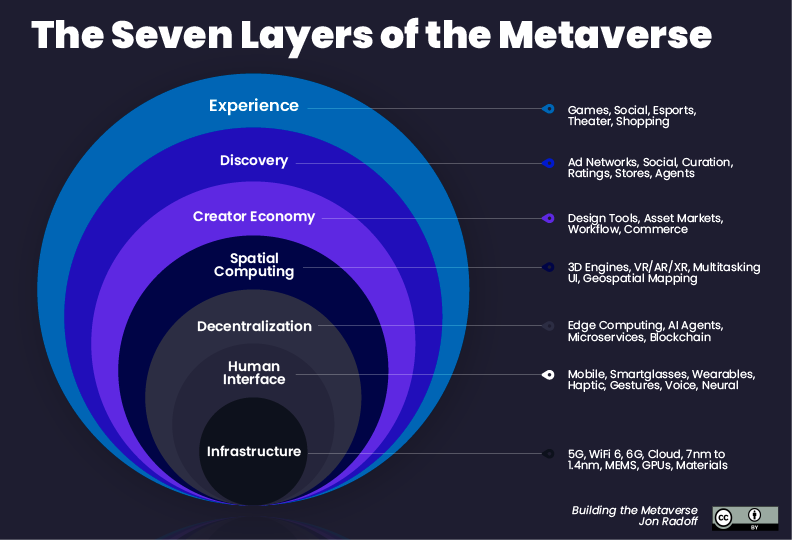
Jon Radoff in his article, the Metaverse Value Chain, states seven important layers to the metaverse becoming a fledged establishment.
If looked at closely, Epic has quietly been building to own the software and experience stack from the Experience Layer down to the Spatial Computing layer.
Experience
The key insight into the Epic building a great metaverse experience stems from Fortnite’s recent transition to a social network rather than just a game through their Party Island mode. Earlier, teenagers and the millennial generation kept in touch with their friends by message or phoning each other. Fortnite changes that. Now, they “digitally hang out” on Fornite and the best part is that conversation isn’t limited to just games. It’s about school, work, music, the hottest gossip in town and more. The game's lack of a specific plot or intellectual property allows for more open-ended conversation. What Epic has also done really well is mastered the gameplay and feeling across platforms. This means whether you own the cheapest Android mobile device or a $1000+ power-packed gaming laptop, users from all stratas and economic classes of society will come together on Fortnite.
At some point, Fortnite may start supporting digital stores for brands like Nike, Adidas and start streaming content from partners like Disney. This would mean all kinds of free-time activity from all age groups and economic classes would culminate on Fornite making it the place boundaries between digital and physical life are broken.
Discovery
With 83 million monthly active users(MAUs), Epic’s metaverse in the form of Fortnite(for now) is eye-catching digital advertising real estate. What Epic can use to their advantage is that it can lead the way for creative and non intrusive advertising. Most advertising that exists today is in the form of mini audio/video ads between content consumed on platforms like Spotify or YouTube.
If you’ve seen the famous network effect diagram Walt Disney had drawn out for Disney’s business plans, it’s fairly easy to see how this can apply to Epic’s discovery network. Through Fortnite(analogous to Disneyland), Epic can leverage its virtual avatar characters to its advantage by partnering with top clothing brands to showcase latest fashion drops. This would especially appeal to younger generations up to date with the latest Jordan drops or NFL/MLS jerseys. Here, it could also plug in upcoming movies or album drops in the form of avatars dressed up like animated characters(think Marvel) or song artists which can create a lot of buzz for such content.
The recent Travis Scott concert on Fortnite paints a clear picture as to how Epic aims to power discovery and virtually distribute the best artists worldwide. Though it was a ten minute spectacle, the Travis Scott concert saw 12.3 million concurrent users on the platform and marked the release of Travis’ new album “Astronomical”. One of the biggest reasons both parties would’ve joined to make such a deal come through would’ve been is the immense reach Travis gets with no geographical boundaries limiting his release on a virtual playground like Fortnite while Epic wins from the astronomical(pun intended) success of the concert in attracting bigger stars and a wide variety of events leading the way of making classy digital events come true.
Spatial Computing
Spatial computing is a concept that combines real-world and virtual-world computing, breaking down the barriers between the physical and ideal realms. This can be achieved by either integrating physical space into the computer or injecting computing capabilities into physical objects.
With Unreal Engine, Epic almost owns the development of spatial computing spaces in the software world. For reasons as listed above in the “Technological Superiority” section and with acquisition of 3D assets companies such as Sketchfab, it’s clear that Epic wants to own/already owns a major chunk of the spatial computing infrastructure that will power the metaverse. What seems key is that once the metaverse is built on top of the first few infrastructure platforms, it’ll require a lot of effort and money to switch over to another network.
Unreal-based infrastructure has a major advantage when it comes to networks: the ability to connect various products, worlds, and experiences to one another. For example, Epic’s latest collaboration with Ferrari means that Epic could easily drop the ultra-realistic Ferrari model it created on Unreal into Fortnite and link it with merchandise Ferrari might want to sell. Similarly with music/video platforms Epic is building on top of Unreal, it’ll be very easy to analyze the data from such experiences to power not only partnerships but generate tools it could create for developers to create similar experiences for other artists and films. Additionally, with music and video platforms that Epic is constructing on top of Unreal, analyzing data from such experiences will enable the development of tools not only for partnerships but also for enabling creators to develop similar experiences for other artists and films.
Downsides/The Bear Case
Over reliance on Fortnite/Sustaining Fortnite Statistics
Approximately 70% of Epic Games' revenue in 2020 came from Fortnite, down from 97% in 2018, the year Fortnite’s MAUs peaked. Though Epic shows a declining reliance on Fortnite by expanding into revenue streams from Unreal Engine, Epic Games, the Epic Online Services and new game titles like Fall Guys and Rocket League, their share in Epic’s revenue model hardly makes up 20%.
At the same time, as seen in the chart below, Fortnite’s average monthly players has dropped by 40 million users while also seeing a decline in peak players per day. This can be attributed to video game fatigue where players and research report playing a similar kind of shooting game can lead to exhaustion thus causing decline in the metrics above as Epic strengthens its ambitions in the metaverse.
Further, Epic is taking a massive bet with the metaverse being the future of Fortnite. The bet on people spending most of their digital lives - shopping, creating/consuming content, gaming - on Fortnite can get exhausting. The following chart describes where Fortnite may be in its user journey. It seems to have crossed its user growth stage where through the pandemic it amassed several users and is in a crucial period of sustaining the user base while transitioning to the metaverse. While the number of registered players may be on the rise every year, it is important to realize that in-game spending most likely comes from dedicated users and sustaining these paying users will help maintain Fortnite’s extraordinary revenue numbers that have subsidized Epic’s other ventures such as the Games Store where it follows a loss leader approach.
Loss Leader Position with Epic Games Store
Epic started its Games Store as a way to better distribute its own games without any intermediary fees and expanded it to other games where they undercut Steam by only taking a 12% cut on revenues compared to Steam’s 30%.
While EGS is popular among developers and players partly because of its generous benefits, which include low royalties, minimal guarantees, and weekly free games, this has also driven up its acquisition costs quite a bit. In its 2020 Year in Review, Epic stated that EGS users would claim over 749 million free game copies. If those games were sold normally, even at discounted prices, they would be worth billions of dollars. At the same time, Epic would’ve paid substantial amounts to get these games to be traded on EGS. Some claim EGS paid a whopping $444 million in minimum pay guarantees while earning in 2020 while earning only $95 million till the end of 2020. It does not take a financial genius to see how this can be unsustainable in the long run and may end up being a profitless venture if what CEO Tim Sweeney says is true that he’d abandon EGS if Steam reduced its revenue share.
Summary
Epic has a track record of adapting its business model to evolving consumer demands. Yet, there are still a number of issues that must be addressed. They include assuring Fortnite's relevance, sustaining the EGS, retaining both developers and gamers, and staying ahead of emerging competitors like as Meta, Apple, and NVIDIA as gaming businesses enter the tech industry.
Although these problems are difficult to overcome at the same time, Epic Games has expertise overcoming severe hurdles. Their gaming section and Unreal Engine are the culmination of decades of hard labor, and they have only recently begun to explore the possibility of a much bigger market.